Reverse Engineering — 3D Scan to CAD, Part Reproduction & Legacy Documentation
Reverse Engineering — 3D Scan to CAD, Part Reproduction & Legacy Documentation
Reverse engineering is the process of recreating or producing 3D models or 2D documentation for a physically existing part or component by editing data obtained from 3D scanning.
MDP Engineering provides professional reverse-engineering services — reconstructing existing components into full 3D CAD models, producing 2D/3D technical documentation, and enabling part reproduction, redesign or integration into modern production systems.
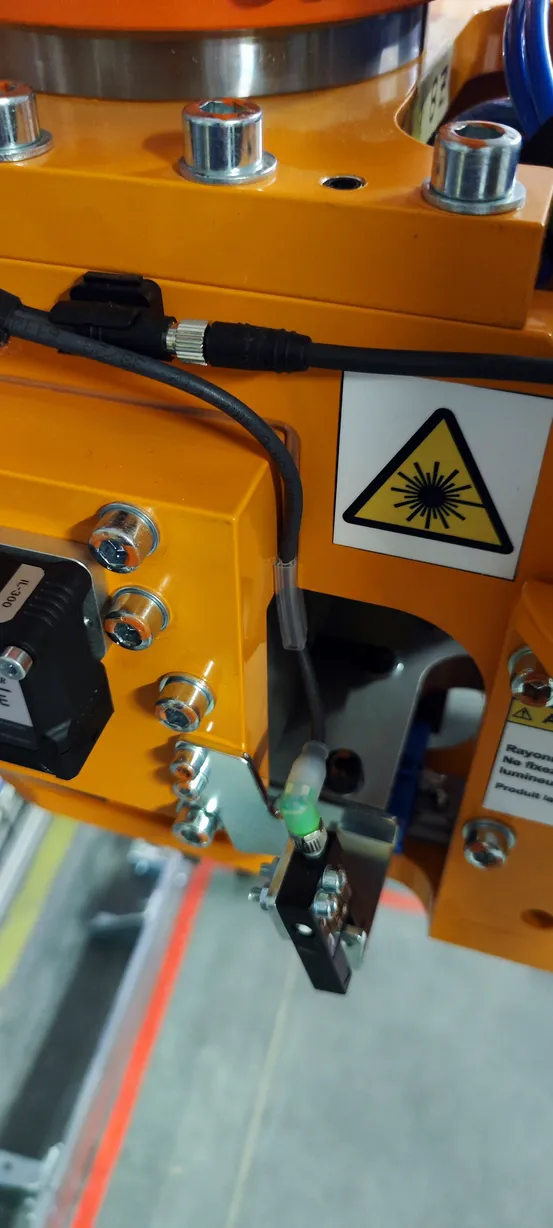

3D Scanning for Industry. Creating a Virtual Image of a Component and Converting it to a CAD Model.
To enable the future development of a product’s physical structure, it’s necessary to digitize its surface and create a CAD model that can then be freely modified and optimized in a computer program. In the context of the services we provide, this is the process of obtaining fully editable 3D models of parts (or 2D technical drawings) that are compatible with any CAD software. These models are developed based on data from 3D scanning. The models can be used to produce replacement parts, improve part fit, or serve as a starting point for designing new components (re-design).
At MDP Engineering, we specialize in using this reverse engineering method to create precise digital models, technical documentation, and to reproduce components that may be difficult to acquire or are no longer manufactured. We offer a comprehensive range of reverse engineering services tailored to our clients’ individual needs.
The Reverse Engineering Process
Our reverse engineering process is precise and well-structured, guaranteeing high-quality results. It consists of the following stages:


Assessment and Planning:
We work with the client to define the project goals, scope of work, and expected outcomes.
Data Acquisition:
We use advanced 3D scanners or traditional measurement methods to collect precise data about the object.
Data Processing:
We convert the raw data into useful formats, such as point clouds or mesh models.
CAD Modeling:
We create precise digital models that can be used for production, analysis, or archiving.
Verification and Testing:
We check the models for accuracy and functionality, making any necessary corrections.
Documentation and Support:
We provide full technical documentation and offer support during implementation or production.
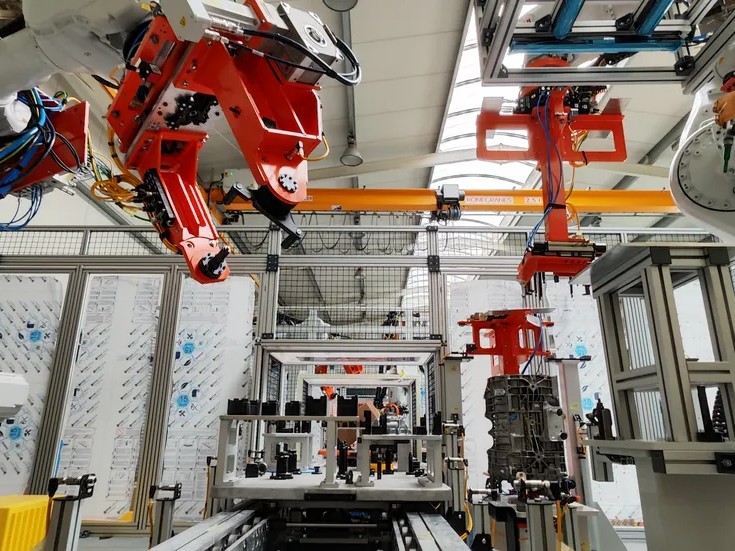

3D Scanning and Digitization of Physical Objects:
We transform real-world objects into accurate digital data to improve their function and optimization.
CAD Model Creation
Based on scans or measurements, we develop detailed models ready for further use.
Analysis and Reproduction of Mechanical Components:
We examine the structure and functionality of parts to faithfully recreate them.
Reconstruction of Spare Parts:
We restore machine and equipment components to a usable state, even if they are no longer available on the market.
Project Optimization:
We improve existing designs in terms of efficiency, production costs, or durability.
What Problems Does Reverse Engineering Help Solve?
Reverse engineering addresses specific challenges faced by clients:
- Difficulty in acquiring spare parts: By reproducing components, it eliminates the problem of unavailability of parts for older equipment.
- High production costs or low efficiency: Design optimization reduces expenses and increases efficiency.
- Lack of technical documentation: It provides comprehensive data, making it easier to manage and maintain systems.
- Slow reaction to market changes: It accelerates product development, enabling quick adaptation to new requirements.
- Risk of losing heritage: It safeguards artifacts through their digital preservation.
How Reverse Engineering Helps Clients
Problems with part fit – Reverse engineering ensures a perfect fit of the new component with the existing structure, eliminating the need for manual adjustments.
Brak dokumentacji technicznej – stworzenie modelu CAD i rysunku technicznego zabezpiecza możliwość przyszłej produkcji lub modyfikacji detalu.
Examples of Reverse Engineering Applications
Reverse engineering can be applied to:
- Castings, molds, tools, sand and wax cores
- Molded parts, dies, and components made of plastics, carbon fiber, and composites
- Stampings, dies, sheet metal, and welded parts
- Car parts, body panels, rims, interiors, and entire vehicles
- Boat hulls, yacht cabins, motorboats, and jet skis
- Motorcycles, bicycles, and their frames
- Semitrailers, trailers, and agricultural machinery and tools
- Steel structures, welded constructions, large and high-tonnage castings
- Turbines, hubs, shafts, rotors, and blades
Reverse engineering enables the digitalization of nearly any type of industrial part or component. We perform scanning and documentation for items with various material structures and levels of geometric complexity. Advanced 3D technologies allow us to cover both precise mechanical parts and large-scale steel constructions. Projects may involve single components or entire assemblies that require integration into production lines.
Key types of parts:
Castings and molds
Tools, plastic, composite, and sheet metal components
Automotive and motorcycle parts
Boat hulls, bicycle and vehicle frames
Industrial elements: turbines, shafts, rotor blades
Large-scale steel structures
Yes, reverse engineering is the perfect solution when technical documentation is incomplete or completely missing. We generate full 2D and 3D documentation based on a scanned part, ensuring accurate reconstruction of geometry, dimensions, and material properties. This process greatly simplifies parts management, reproduction, and the design of replacements or upgrades for existing machinery. Using 3D scanning and advanced CAD tools, our engineers create documentation that complies with industrial standards, providing a ready foundation for production or integration with the client’s manufacturing lines.
Reverse engineering is widely used across various industrial sectors, offering measurable benefits in both maintenance and new project development. It is applied to reproduce worn machine components, repair damaged parts, and precisely fit new parts into existing systems. This approach is invaluable for production line upgrades, where improvements must be integrated without halting operations. It also facilitates the digitalization of technical heritage, ensuring that information on historical designs is preserved for future use. Furthermore, it enables the design of replacements and structural changes (re-design), leading to greater efficiency and reduced production costs.
Reverse engineering effectively addresses numerous production challenges. It provides solutions for machine downtime caused by the unavailability of original parts or incompatibility of available replacements. It helps reduce high unit production costs by optimizing designs and implementing more efficient manufacturing methods. We also solve situations where technical documentation is missing, enabling the reproduction or modernization of a component. Reverse engineering ensures fast adaptation to market changes, shortens implementation times, and secures vital information about products no longer supplied by the original manufacturer. As a result, companies gain greater independence and operational continuity.
Simply define your needs – whether it concerns reproducing a part, preparing technical documentation, or carrying out a comprehensive project optimization. We conduct a technological audit and select solutions tailored to your budget and deadlines. The process begins with a detailed analysis of the existing component or system, including 3D measurements and material assessment. We then prepare precise technical documentation that can be used for reproduction, modification, or modernization. At every stage, we maintain close communication with the client to ensure that the developed solutions fully align with their expectations and technical requirements.
